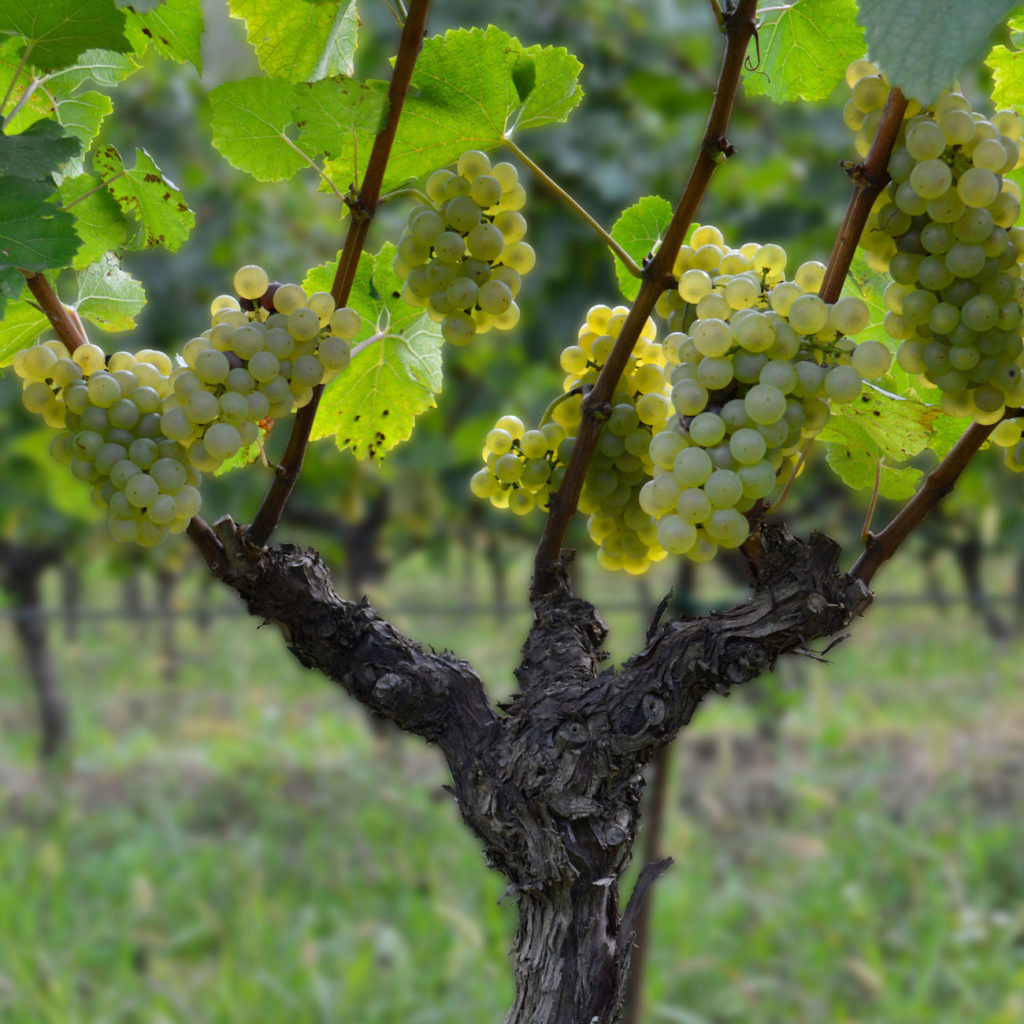
VINE PRUNING
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS AND TRAINING SYSTEMS
It is difficult to observe plant growth and state rigorous, biological rules to explain plant development. The vine is kept in the growth form chosen by the winegrower with pruning cuts. Pruning wounds have to be able to close fast in order to avoid or reduce the formation of dry sections in the conductive tissue. The two main pruning objectives: preserving CONDUCTIVE TISSUE (leggi di più) and hindering ACROTONY. Plants react differently depending on the breeding method used, although these two principles are key to healthy vineyard and grapes. Preserving conductive tissue will lower degenerative wood diseases incidence. A well-distributed, bundling free, leaf wall will be obtained if acrotony is hindered.
Vegetative point
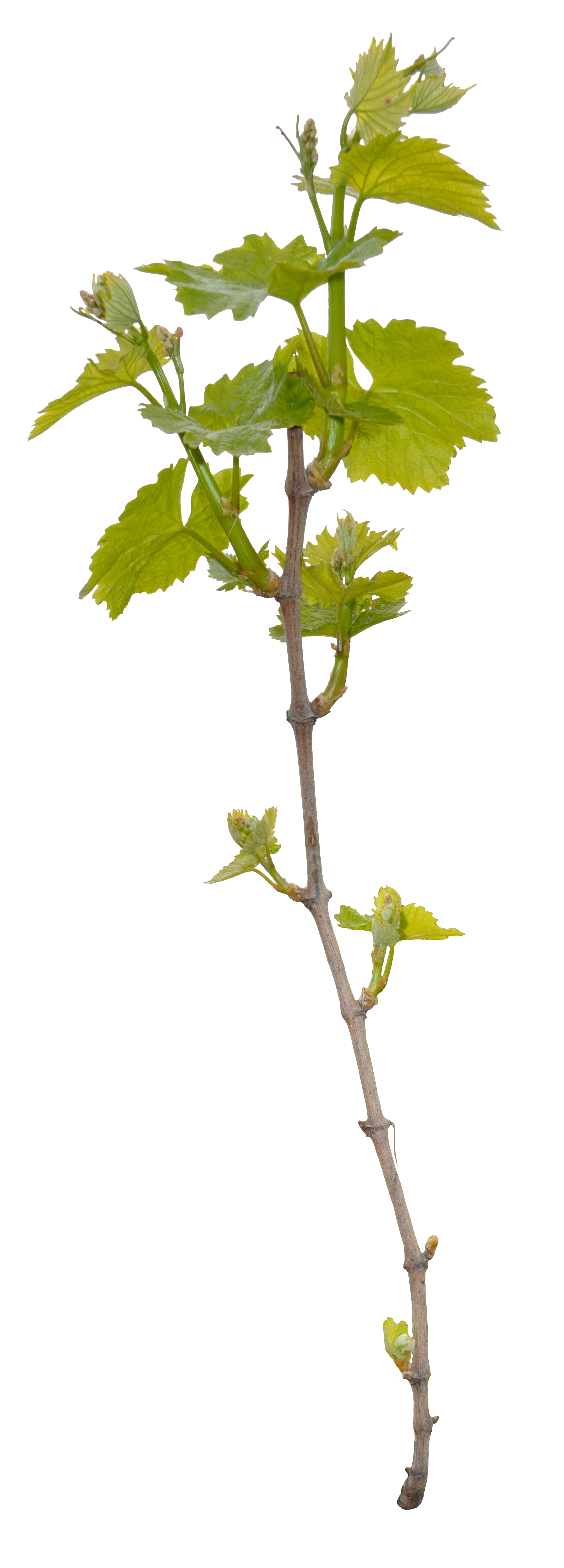

Acrotony
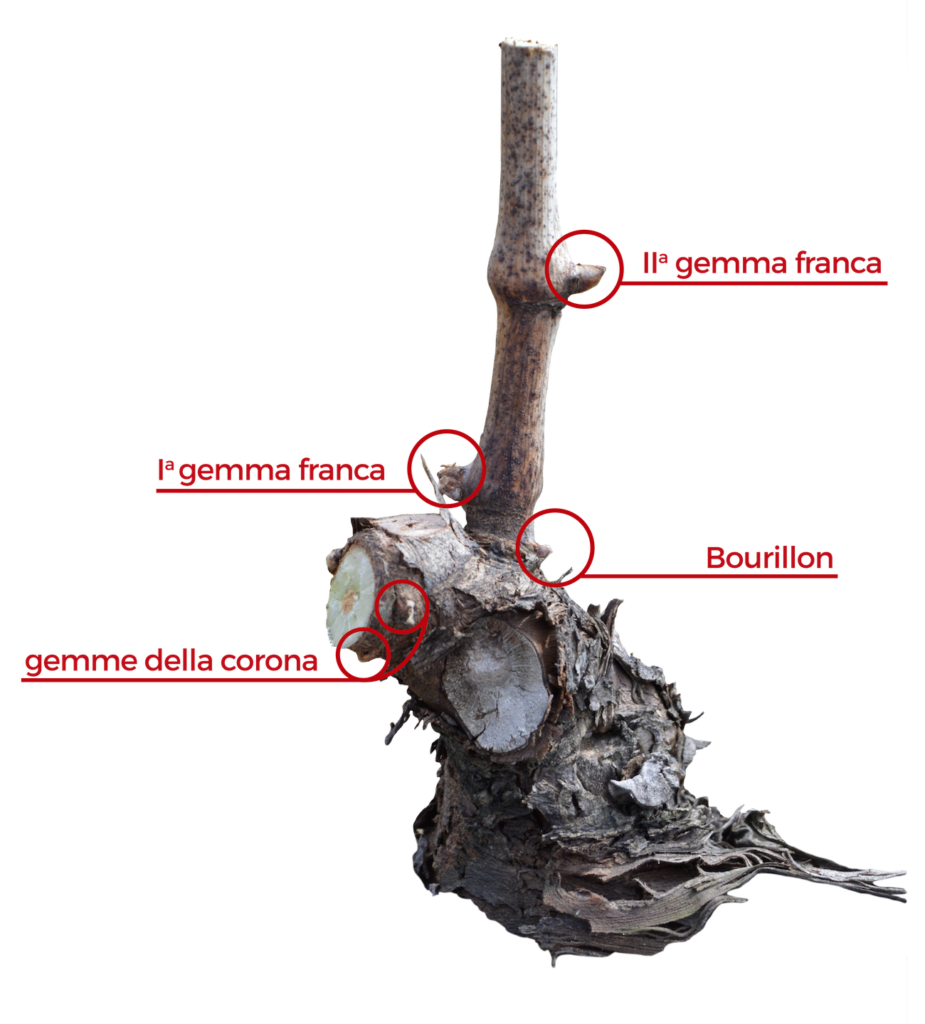
Whether the company chooses HEAD or CORDON breeding, it should still identify, organize and preserve VEGETATING SHOOTS, thus avoiding forced branching. The ALBERATE training is the only type of training with trunk branches.
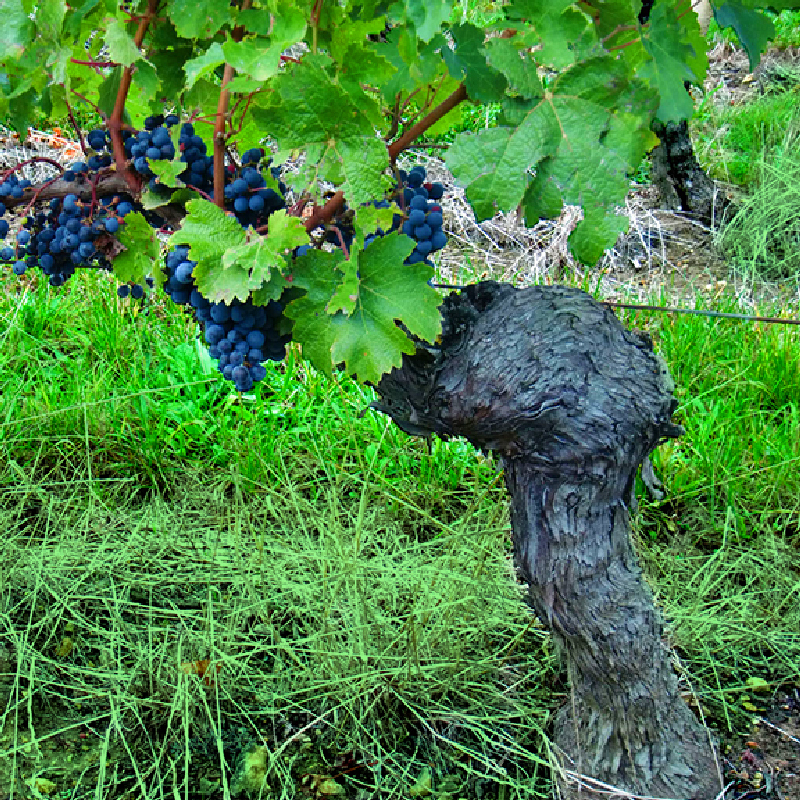
GUYOT
This form of breeding consists in inserting a spur and one or two fruit-canes on the head.
GOBELET
The vegetating shoot is placed on top of the branch originating from the same vegetating shoot growth.
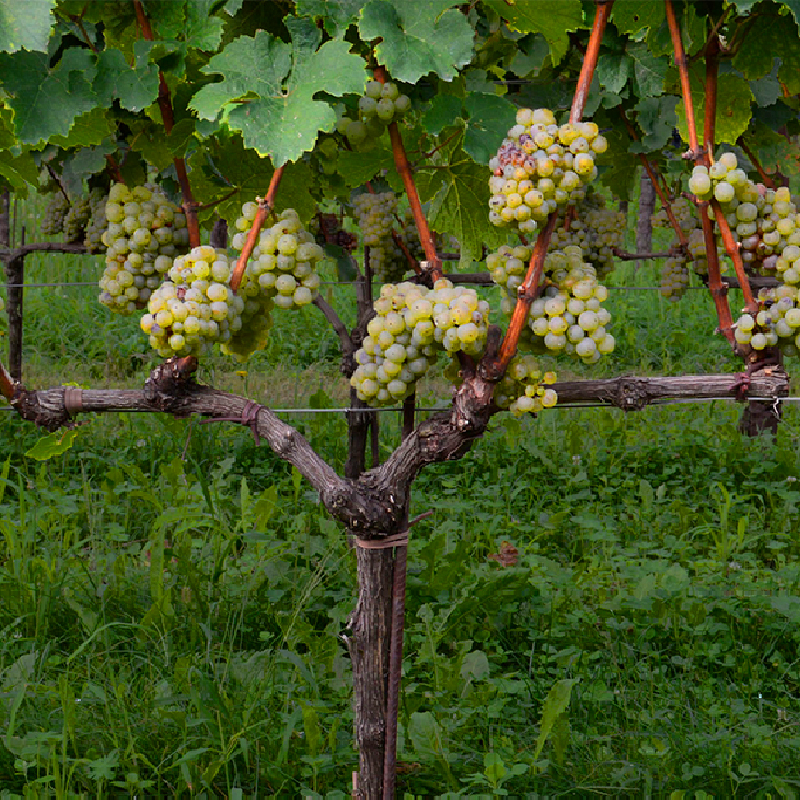
CORDON TRAINED
Spurs starting from the cordon, which in this case is an extension of the trunk, are a source of production.



